This article is for you if you want to know about GRE work and rate problems along with variables in the choice problems with examples. It will spoon-feed you!
GRE Work and Rate Problems
Work and rate problems are among the most common question types in the GRE Quant section, often involving collaboration, partial work, or efficiency comparisons. To overcome these problems, you need to understand the theory, formulas, and strategies for solving them.

Core Theory of Work and Rate Problems
The central formula for work and rate problems is:
Work (W) = Rate (R) × Time (T)
two other essential relationships:
- Rate (R) = Work (W) / Time (T)
- Time (T) = Work (W) / Rate (R)
For time consideration:
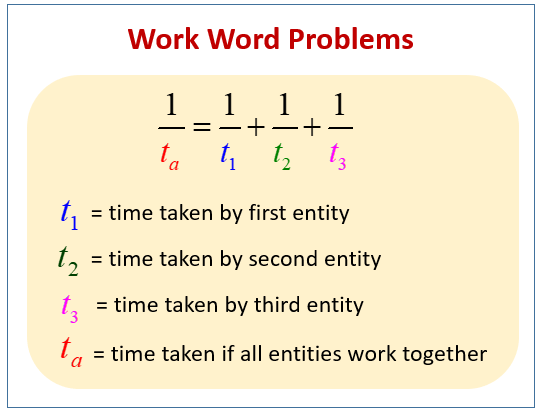
Breaking Down the Components
- Work (W):
Represents the total task or job. Typically, in GRE problems, the total work is considered 1 unit (completing the entire job). - Rate (R):
Refers to how much of the work is completed in one unit of time. For example, if a person completes 1/5 of a task per hour, their rate is 1/5. - Time (T):
The duration it takes to complete the task, either alone or collaboratively.
Types of Work and Rate Problems

1. Single Worker Problems
In these problems, one person or machine completes a task at a constant rate.
Example:
If John can complete a task in 6 hours, how much of the task does he complete in 2 hours?
Solution:
2. Multiple Workers Collaborating
When multiple workers or machines work together, their rates are added.
Key Formula:
Example:
Worker A can complete a task in 5 hours, and Worker B can complete the same task in 3 hours. How long will it take them to complete the task together?
Solution:
3. One Worker Helping Another Midway
In these problems, one worker starts the task, and another joins after some time.
Example:
Worker A can complete a task in 6 hours, and Worker B can complete the same task in 4 hours. Worker A works alone for 2 hours, then Worker B joins. How long does it take to complete the task?
Solution:
4. Inverse Rate Problems
These problems involve workers with varying efficiencies working at different rates.
Example:
If Worker A takes twice as long as Worker B to complete a task, and together they can complete the task in 4 hours, how long does it take each to complete it individually?
Solution:
Work Rate Examples
Question 1

Solution:

Question 2

Solution:

Question 3

Solution:

Question 4

Solution:

Question 5

Solution:

Question 6

Solution:

Question 7
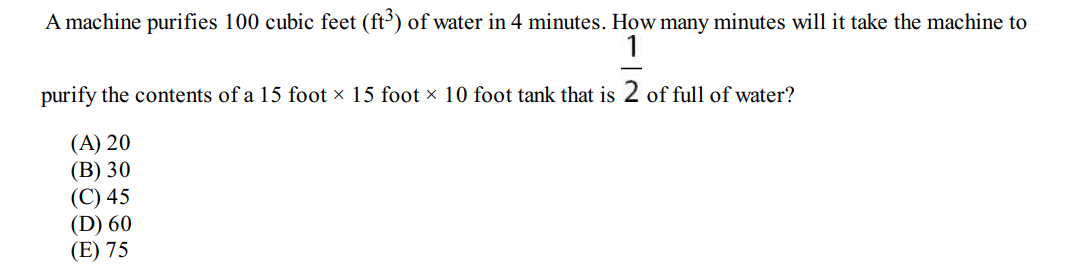
Solution:

Question 8
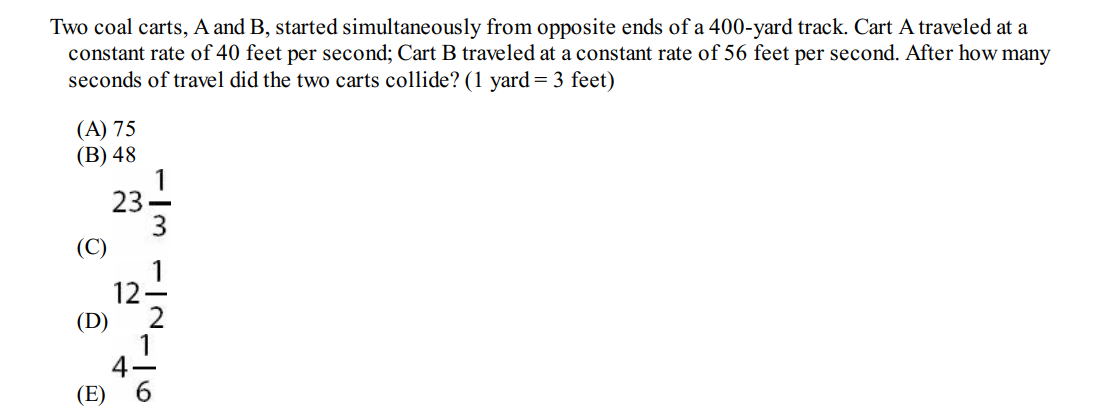
Solution:
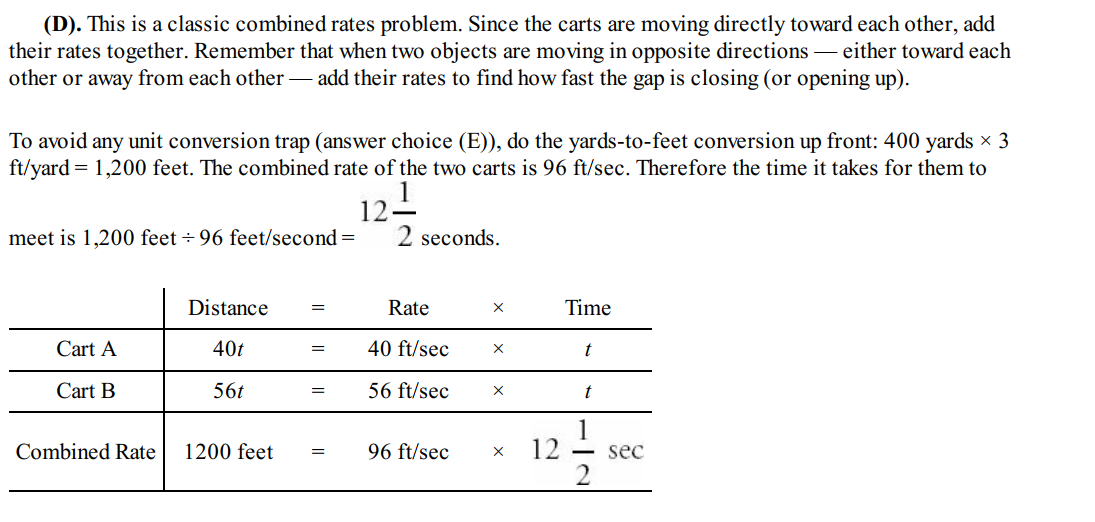
Question 9

Solution:

Question 10

Solution:
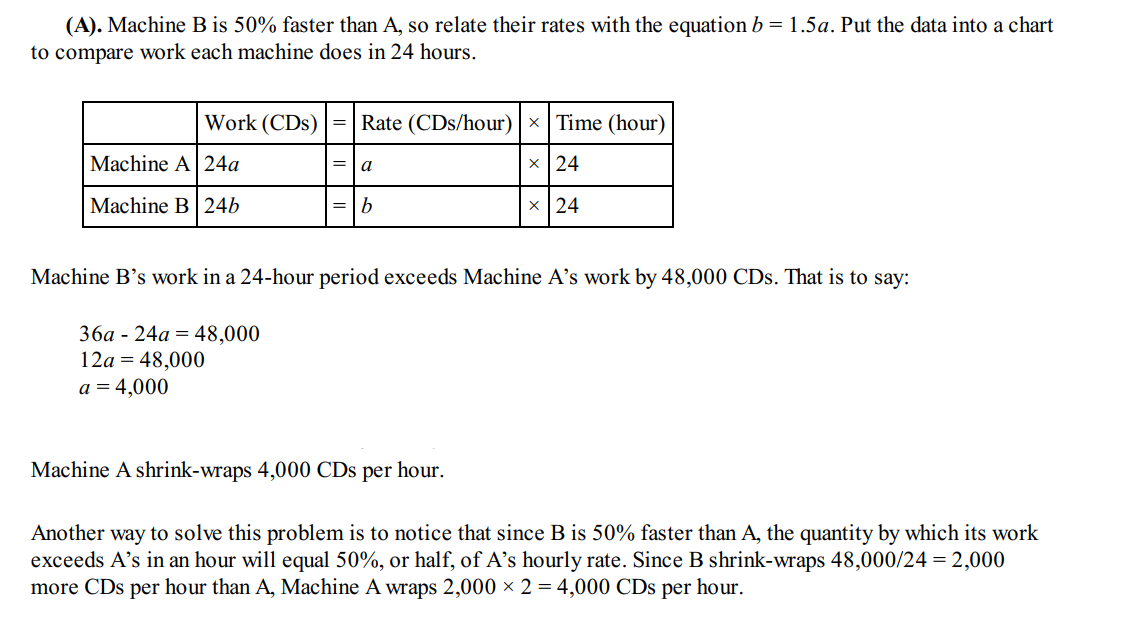
Question 11

Solution:


What Are "Variable in the Choices" Questions?
In these problems, the answer choices are presented as expressions or equations involving variables rather than as fixed numerical values. You are typically asked to simplify, analyze, or manipulate these expressions to find the correct answer.
Examples of Answer Choices
Take a look:
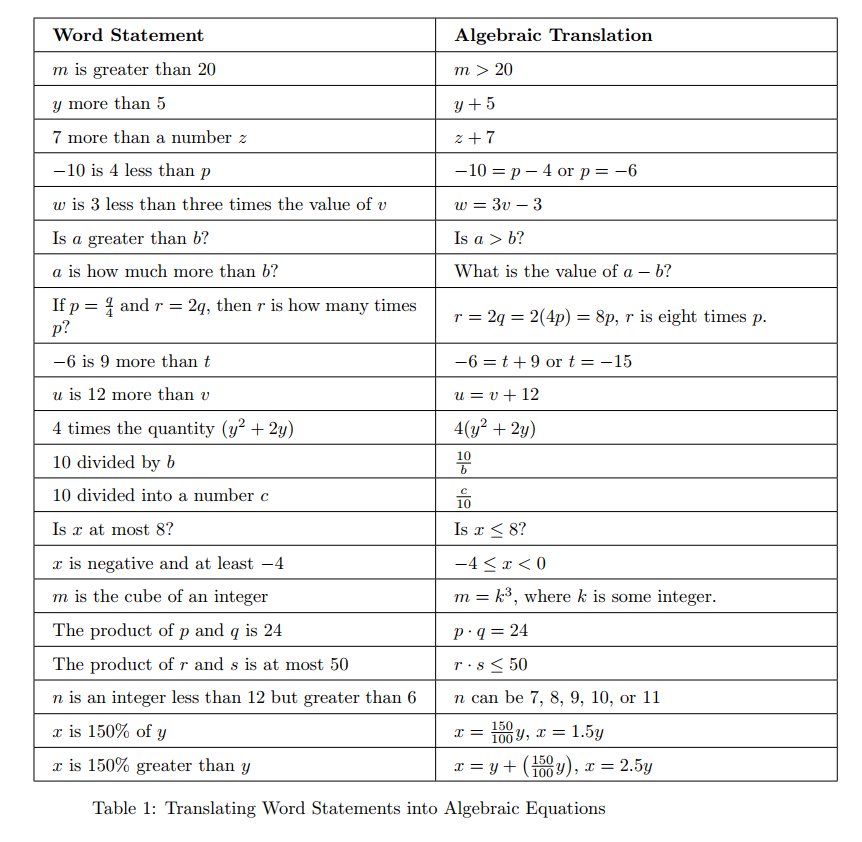
Core Approach to Solving These Problems
- Understand the Question Statement
Carefully analyze what the problem is asking. Is it a relationship between two variables? Are you solving for a specific expression? - Simplify the Problem
Reduce any given equation or expression to its simplest form before working with the answer choices. - Substitute Smart Values
Substitute simple, easy-to-use numbers (e.g., a=1,b=2) into the question and the answer choices. This approach is called the Plug-and-Test Method and is highly effective. - Eliminate Incorrect Choices
Use the process of elimination to rule out answers that do not match your substitutions or simplify incorrectly. - Generalize the Solution
If substituting values doesn't yield an answer (or the problem explicitly prohibits it), work through the algebra symbolically to arrive at the correct expression.
Types of Problems
Simplification-Based Questions
Question:
The average of two numbers is (a+b)/2. If the average of a and 2b is 12, what is the value of a+b?
Solution:

2. Testing Values in Variables
Example:
If x+y=5, which of the following expressions equals x^2+2xy+y^2 ?
Answer Choices:
Solution:
The given problem involves recognizing algebraic identities:
Strategies for Variable-Based Questions
- Memorize Key Algebraic Identities
- Plug-and-Test with Simple Numbers
Choose values like a = 2, b =1 to simplify expressions and verify the answer choices. - Work Symbolically if Necessary
If substitutions are restricted or unclear, use algebra to manipulate the equations.
Variable in the Choices Examples
Question 1

Solution:

Question 2

Solution:

Question 3
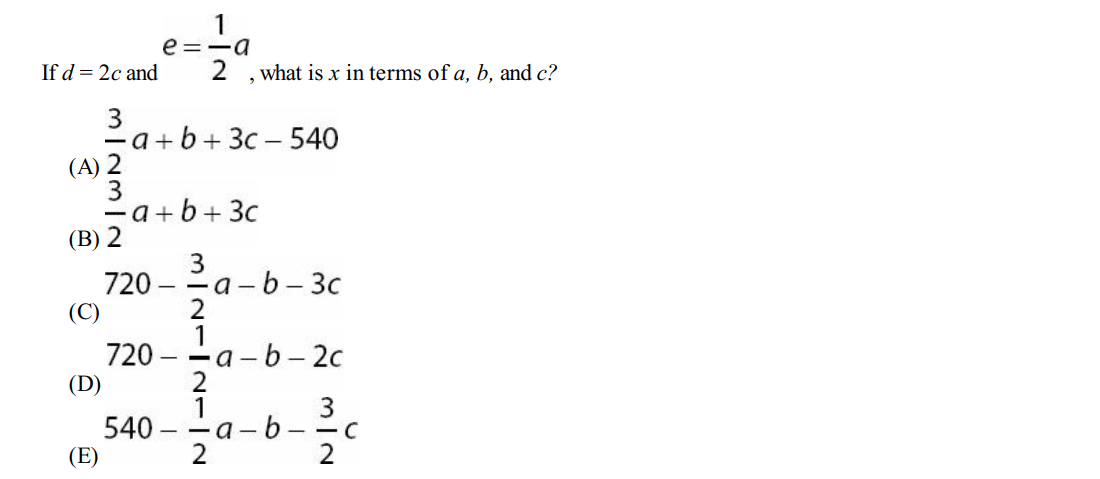
Solution:


Question 4
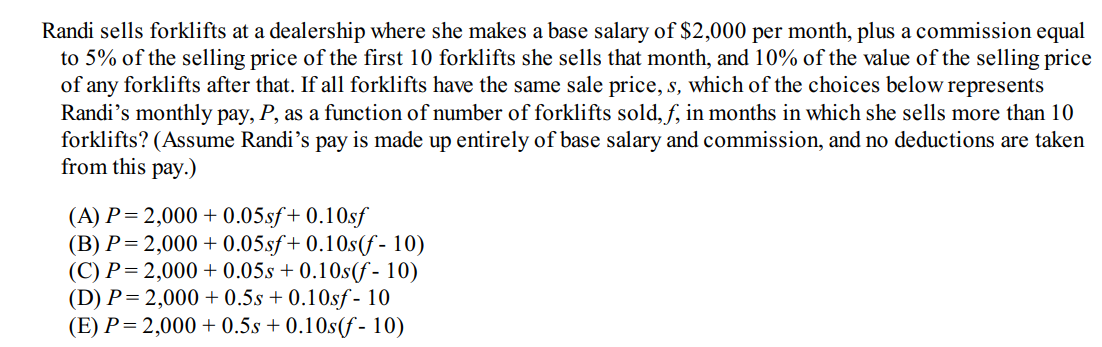
Solution:

